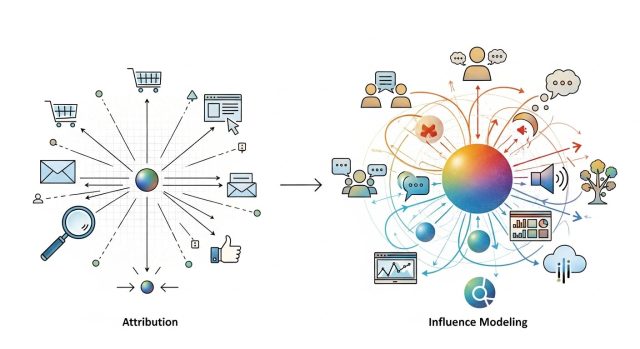
Marketing Measurement Evolution moves beyond traditional attribution to provide a holistic view of marketing impact across time, touchpoints, and channels. Influence modeling integrates both qualitative and quantitative insights, revealing indirect and cumulative effects often missed by attribution alone. By adopting this approach, organizations can optimize strategies, improve ROI, and demonstrate marketing’s broader strategic value.
Marketing Measurement Evolution reflects the ongoing shift in how organizations evaluate the impact of their marketing activities. Traditional attribution models, which allocate credit to specific touchpoints, provide a limited view of marketing effectiveness in today’s multi-channel, multi-device world. Influence modeling expands measurement beyond conversions, considering perception shifts, consideration milestones, and the broader context in which decisions occur. By integrating quantitative and qualitative insights, extending the time horizon of analysis, and mapping interconnected touchpoints, Marketing Measurement Evolution provides a more holistic understanding of marketing’s role in shaping customer behavior and long-term business outcomes. These frequently asked questions aim to clarify key concepts, benefits, challenges, and practical steps for implementing this advanced approach.
The Attribution Crisis

Traditional attribution models emerged during a simpler digital era, when marketing channels were fewer, consumer journeys were shorter, and data collection was relatively straightforward. These models aimed to assign specific conversion credit to marketing touchpoints, helping marketers determine which channels deserved budget, attention, and strategic focus.
Over time, attribution models evolved from basic last-click approaches to more sophisticated multi-touch systems. Multi-touch attribution promised a more accurate distribution of credit across the customer journey, reflecting the reality that multiple interactions contribute to conversion. More recently, machine learning–driven attribution emerged, analyzing massive datasets to attempt predictive credit allocation.
However, despite increasing sophistication, attribution models have continued to face fundamental limitations:
- Cross-device journeys: Consumers often engage with brands across smartphones, tablets, desktops, and in-store experiences, creating fragmented data that attribution struggles to consolidate.
- Walled gardens: Platforms like social media networks control much of their data, leaving attribution systems with blind spots and incomplete insights.
- Expanding touchpoints: The sheer variety of interactions—from podcasts and influencer content to offline events—makes complete tracking nearly impossible.
- Simplistic assumptions: At the core, attribution assumes that conversions can be meaningfully divided among discrete touchpoints. In reality, consumer decision-making is interconnected, non-linear, and influenced by many subtle factors.
These limitations highlight a critical insight in the Marketing Measurement Evolution: attribution alone is insufficient for understanding the true impact of marketing efforts.
Understanding Influence Modeling
Influence modeling represents a major leap forward in the Marketing Measurement Evolution. Unlike attribution, which focuses on assigning conversion credit, influence modeling seeks to understand how marketing activities shape consumer perceptions, preferences, and behaviors over time. For more insights, you can explore advanced marketing analytics tools.
This approach recognizes that customer decisions emerge from complex networks of influence rather than linear paths. For example:
- Some touchpoints create initial awareness.
- Others build credibility or trust.
- Certain influences operate explicitly, while others affect decisions subtly or even subconsciously.
At InboundMarketo, we’ve observed how influence modeling uncovers marketing impacts that traditional attribution consistently misses—especially in scenarios involving high-consideration purchases, long decision cycles, or multi-channel engagement.
Where attribution asks, “Which touchpoint deserves credit?”, influence modeling asks, “How did various factors shape this outcome?” This shift in perspective fundamentally expands what marketers can understand about their campaigns, reflecting a critical step in the ongoing Marketing Measurement Evolution.
The Conceptual Foundations of Influence Modeling
Influence modeling draws on several intellectual traditions that offer richer insights than the click-to-conversion logic of traditional attribution:
- Network Theory: This perspective examines how information, ideas, and preferences spread through interconnected systems. Marketers can see how influence propagates beyond immediate touchpoints to shape broader brand perceptions. Learn more in network theory applications in marketing.
- Behavioral Economics: Human decision-making is affected by cognitive biases, context, and framing effects. Influence modeling accounts for these factors, explaining why identical marketing exposures often lead to different outcomes. You can explore behavioral economics frameworks for marketing.
- Systems Thinking: By emphasizing relationships and patterns over isolated events, systems thinking highlights how marketing activities generate emergent effects greater than the sum of individual touchpoints—effects that attribution fundamentally cannot capture. Check systems thinking in business.
Through these frameworks, influence modeling aligns with the modern reality of marketing: dynamic, multi-dimensional, and interconnected. It represents the next stage in the Marketing Measurement Evolution, empowering marketers to measure impact more holistically and make better-informed decisions.
The Practical Shift to Influence Measurement
Moving from attribution to influence modeling requires both conceptual and practical shifts in how marketing is measured and evaluated. This transition represents a critical stage in the broader Marketing Measurement Evolution, reflecting the increasing complexity of consumer behavior and multi-channel interactions in modern marketing.
Marketers must expand measurement beyond simple conversion events to include perception shifts, consideration milestones, and contextual factors that shape decisions. These intermediate outcomes often prove more actionable than final conversion metrics alone. Understanding these subtler effects is a central aspect of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, as it emphasizes evaluating influence rather than just immediate results.
The time horizon for measurement necessarily extends to capture subtle influences that unfold gradually. Where attribution typically focuses on short-term conversion windows, influence models track how marketing shapes decisions over months or even years. This longer-term perspective is essential to the Marketing Measurement Evolution, enabling organizations to capture cumulative impacts of campaigns that attribution methods often miss.
Most importantly, influence modeling integrates qualitative insights alongside quantitative tracking. Customer interviews, surveys, and observational research provide critical context that explains the “why” behind behavioral patterns. Incorporating qualitative data is a hallmark of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, ensuring that marketers understand both the numbers and the human motivations behind them. For further reading, explore customer insights research methods.
Building Your First Influence Model
While comprehensive influence modeling requires sophisticated methodologies, organizations can begin the transition through focused initiatives that complement existing attribution approaches. Starting small helps teams adopt the necessary mindset shifts central to the Marketing Measurement Evolution without being overwhelmed by complexity.
- Map decision ecosystems rather than linear funnels. Identify all factors potentially influencing purchasing decisions, including non-marketing elements such as product experiences, recommendations, and competitive pressures. This ecosystem-based approach aligns with the Marketing Measurement Evolution principle of recognizing influence as multi-dimensional and interconnected rather than linear and discrete.
- Establish baseline measurements of brand perception, preference drivers, and consideration factors among target audiences. These metrics create the foundation for tracking how marketing activities shift attitudes and preferences over time. Proper baseline measurement is another key component of the Marketing Measurement Evolution.
- Implement marketing mix modeling approaches that account for both marketing and non-marketing factors affecting outcomes. These statistical techniques help isolate true influence patterns from background noise and coincidental correlations. By integrating multiple data sources, organizations move closer to the vision of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, where influence is measured holistically rather than attributed narrowly to individual touchpoints. For methodology guidance, see marketing mix modeling examples.
The New Measurement Toolkit
Influence modeling draws on diverse data sources that extend far beyond the click streams and conversion pixels of traditional attribution. These tools represent the practical backbone of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, enabling marketers to capture subtle and multi-channel effects.
- Brand tracking studies provide longitudinal insights about how marketing shapes perceptions and preferences over time. These studies reveal attitudinal shifts that precede behavioral changes and are often invisible to attribution models.
- Social listening tools capture how messages spread and evolve through networks, illuminating influence patterns that traditional approaches completely miss. They help identify hidden amplifiers or dampeners of marketing impact, reflecting the growing sophistication in the Marketing Measurement Evolution. Learn more about social listening tools for marketers.
- Path analysis techniques map complex relationships between variables, revealing how influence flows through interconnected touchpoints. These approaches allow marketers to understand sequencing effects where the impact of one touchpoint depends on prior exposures, reinforcing the central premise of the Marketing Measurement Evolution.
Challenges in Implementation
The transition to influence modeling presents several challenges that organizations must navigate thoughtfully.
- Data integration: Influence modeling requires connecting touchpoint data with attitudinal metrics, competitive intelligence, and contextual factors that often reside in separate platforms. Overcoming this challenge is critical to achieving the goals of the Marketing Measurement Evolution.
- Organizational resistance: Teams accustomed to attribution may struggle with the nuanced insights that influence models provide. Education and change management are vital to advance the Marketing Measurement Evolution within corporate culture. For best practices, seechange management in marketing analytics.
- Statistical complexity: Influence models rely on advanced techniques, such as regression analysis, structural equation modeling, and network-based methods. Organizations may need to build new analytical capabilities or partner with specialists during this transition. Addressing these technical challenges is part of fully embracing the Marketing Measurement Evolution and unlocking deeper insights.
Case Example: Influence Modeling in B2B Marketing
A B2B technology firm provides a clear example of the practical impact of moving beyond attribution to influence modeling, illustrating a critical step in the ongoing Marketing Measurement Evolution.
The company’s traditional attribution system indicated declining ROI from industry event sponsorships, suggesting that resources should be shifted to digital channels with more direct conversion paths. However, before making this strategic adjustment, the marketing team decided to develop a basic influence model that incorporated customer interviews, expanded touchpoint measurement, and cross-channel tracking. This approach aligned with the principles of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, which emphasizes understanding marketing impact beyond simple conversion credit.
The influence model revealed insights that attribution alone could not capture. While events rarely led directly to immediate conversions, they significantly amplified the effectiveness of subsequent digital touchpoints. Prospects who attended events were three times more likely to engage deeply with content and twice as likely to respond positively to sales outreach. The model showed that events established foundational trust and credibility, which made other marketing activities more effective. This finding demonstrated a core aspect of the Marketing Measurement Evolution: that influence is often indirect, cumulative, and context-dependent.
Rather than cutting event budgets as attribution suggested, the company redesigned its event strategy to intentionally support follow-up digital engagement. By aligning live interactions with digital nurture programs, the firm increased overall marketing ROI, showing how influence modeling can unlock hidden value and drive smarter allocation of marketing resources. This example illustrates the real-world benefits of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, where decisions are informed by holistic understanding rather than simplistic attribution metrics.
Evolving From Attribution to Holistic Understanding
 Leading organizations recognize that the most effective approach does not abandon attribution entirely but integrates it within broader influence frameworks. This balanced methodology is a hallmark of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, blending tactical clarity with strategic insight.
Leading organizations recognize that the most effective approach does not abandon attribution entirely but integrates it within broader influence frameworks. This balanced methodology is a hallmark of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, blending tactical clarity with strategic insight.
Many firms start by conducting influence studies for specific campaigns or product lines while maintaining attribution for short-term performance optimization. This dual approach allows marketing teams to compare insights, validate influence findings, and gradually build confidence in the methodology. Others extend attribution windows using time decay models to better reflect the longer-term effects of marketing activities—a transition that represents a key phase in the Marketing Measurement Evolution, acknowledging that influence unfolds over extended periods.
Some organizations adopt different measurement approaches for different marketing objectives. For example, they may use attribution to optimize demand generation campaigns while applying influence modeling to brand-building, market development, or customer relationship initiatives. This nuanced approach ensures that every dimension of marketing impact is captured, advancing the Marketing Measurement Evolution by highlighting both direct and indirect effects.
The Organizational Impact
Adopting influence modeling often catalyzes broader organizational change. Marketing teams frequently reorganize around audience segments rather than channels, reflecting the cross-channel and multi-touch nature of influence. This approach overcomes the siloed thinking that traditional attribution systems often reinforce and exemplifies a core principle of the Marketing Measurement Evolution: understanding influence across the entire customer ecosystem.
Planning horizons generally extend as organizations acknowledge that meaningful influence develops over longer timeframes than attribution typically measures. Campaign planning shifts from short-term tactical execution to sustainable strategy development, a hallmark of the Marketing Measurement Evolution. Marketing’s perceived role within the organization often expands as well, moving from a narrow focus on lead generation to broader contributions such as shaping customer relationships, enhancing competitive positioning, and influencing market perception. Influence models make these contributions visible, reinforcing the strategic importance of marketing.
The Future of Marketing Measurement
As influence modeling methodologies mature, several emerging trends are likely to shape the ongoing Marketing Measurement Evolution.
Artificial intelligence increasingly supports influence modeling by identifying complex patterns across diverse data sources. AI tools can detect subtle relationships, uncover previously hidden influence pathways, and highlight shifts in customer behavior earlier than manual analysis. This integration represents a forward-looking component of the Marketing Measurement Evolution, where technology enhances the ability to understand indirect and cumulative impacts.
Privacy regulations and data protection changes accelerate the shift from individual-level tracking to probabilistic modeling approaches. As personally identifiable data becomes less accessible, statistical influence models gain prominence, allowing marketers to measure impact without relying on invasive tracking methods. This shift is another critical phase in the Marketing Measurement Evolution, emphasizing measurement approaches that are both effective and privacy-compliant.
Finally, the integration of qualitative and quantitative methodologies continues to deepen. Organizations are increasingly combining survey data, customer interviews, observational research, and behavioral analytics into unified influence models. This convergence produces richer, multi-dimensional insights than either approach alone, reflecting a sophisticated stage of the Marketing Measurement Evolution where all relevant dimensions of influence are considered.
Conclusion: Embracing Marketing’s True Complexity
The shift from attribution to influence modeling represents more than a measurement evolution—it reflects a fundamental recognition of how marketing actually works.
Marketing doesn’t simply trigger conversions through isolated touchpoints. It shapes perceptions, builds relationships, creates meaning, and influences decisions through interconnected experiences over time.
By embracing influence modeling, marketers develop measurement systems that better reflect this complex reality. This shift leads not only to more accurate measurement but ultimately to more effective marketing that respects the sophisticated nature of human decision-making.
Organizations that successfully navigate this transition gain sustainable advantage through deeper customer understanding, more effective resource allocation, and marketing strategies that create meaningful influence instead of merely chasing attributable conversions.
frequently asked questions
What is Marketing Measurement Evolution?
Marketing Measurement Evolution is the transition from traditional attribution models to influence-based approaches, focusing on understanding how marketing shapes perceptions, preferences, and behaviors across multiple touchpoints and over time.
How does influence modeling differ from attribution?
Attribution assigns credit for conversions to specific touchpoints, whereas influence modeling evaluates how various interactions collectively affect decision-making, often capturing indirect and cumulative effects.
Why is Marketing Measurement Evolution important for modern marketing?
As customer journeys become longer, more complex, and multi-channel, attribution alone fails to capture the full impact of marketing. Marketing Measurement Evolution provides a holistic view, allowing smarter resource allocation and strategy optimization.
What types of data are used in influence modeling?
Influence modeling uses both quantitative data (clicks, conversions, engagement metrics) and qualitative data (customer interviews, surveys, observational research) to understand not just what happened but why it happened.
Can organizations use attribution and influence modeling together?
Yes. Many companies maintain attribution for tactical optimization while implementing influence modeling for long-term strategic insights, creating a complementary measurement framework.
How do you start building an influence model?
Begin by mapping decision ecosystems instead of linear funnels, identifying all factors that influence purchasing decisions, establishing baseline brand and preference metrics, and gradually integrating statistical modeling techniques.
What are the main challenges of adopting influence modeling?
Challenges include data integration across platforms, organizational resistance to less definitive answers, statistical complexity, and the need for longer-term planning horizons.
How does influence modeling affect marketing strategy?
Influence modeling shifts strategy toward audience-focused, multi-channel initiatives, extending planning horizons and emphasizing long-term relationship building over immediate conversion.
How is technology shaping the Marketing Measurement Evolution?
AI and advanced analytics enable marketers to detect complex patterns, uncover hidden influence pathways, and integrate diverse data sources for more accurate, timely insights.
How does Marketing Measurement Evolution address privacy concerns?
By relying more on probabilistic modeling, aggregated data, and statistical analysis rather than individual-level tracking, influence modeling aligns with privacy regulations while still providing actionable insights.